Trigonometric Identities
| sin(theta) = a / c | csc(theta) = 1 / sin(theta) = c / a |
| cos(theta) = b / c | sec(theta) = 1 / cos(theta) = c / b |
| tan(theta) = sin(theta) / cos(theta) = a / b | cot(theta) = 1/ tan(theta) = b / a |
sin(-x) = -sin(x)
csc(-x) = -csc(x)
cos(-x) = cos(x)
sec(-x) = sec(x)
tan(-x) = -tan(x)
cot(-x) = -cot(x)
| sin^2(x) + cos^2(x) = 1 | tan^2(x) + 1 = sec^2(x) | cot^2(x) + 1 = csc^2(x) | |
sin(x 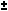 y) = sin x cos y y) = sin x cos y 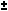 cos x sin y cos x sin y | |||
cos(x 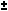 y) = cos x cosy y) = cos x cosy 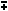 sin x sin y sin x sin y | |||
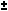 y) = (tan x
y) = (tan x 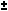 tan y) / (1
tan y) / (1 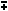 tan x tan y)
tan x tan y) sin(2x) = 2 sin x cos x
cos(2x) = cos^2(x) - sin^2(x) = 2 cos^2(x) - 1 = 1 - 2 sin^2(x)
tan(2x) = 2 tan(x) / (1 - tan^2(x))
sin^2(x) = 1/2 - 1/2 cos(2x)
cos^2(x) = 1/2 + 1/2 cos(2x)
sin x - sin y = 2 sin( (x - y)/2 ) cos( (x + y)/2 )
cos x - cos y = -2 sin( (x - y)/2 ) sin( (x + y)/2 )
| angle | 0 | 30 | 45 | 60 | 90 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| sin^2(a) | 0/4 | 1/4 | 2/4 | 3/4 | 4/4 |
| cos^2(a) | 4/4 | 3/4 | 2/4 | 1/4 | 0/4 |
| tan^2(a) | 0/4 | 1/3 | 2/2 | 3/1 | 4/0 |
Given Triangle abc, with angles A,B,C; a is opposite to A, b opposite B, c opposite C:a/sin(A) = b/sin(B) = c/sin(C) (Law of Sines)
| (Law of Cosines) |
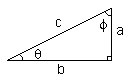
No comments:
Post a Comment